Scoliosis
Appointment Inquiries
Call us at: (877) 222-5348
Definition
A sideways curvature of the spine.
Root Causes
Back Pain or Stiffness, Difference in Hip Height, Difference in Rib Cage Height, Hight Loss, Leg Pain, Numbness, Shoulder Blades stick out, Spinal Texture or Color Changes
Risk Factors
Age, Family History, Gender
Treatments
Anti-Inflammatory Medication, Chiropractic, Cortisone Shots, Electrotherapy, Epidural Injections, Facet Injections, Inversion Therapy, Physical Therapy, Spinal Decompression, Trigger Point Injections
What is scoliosis?
The spine should have a curve, mostly in the neck and lower back, but the good kind of spinal curves are from front to back. Scoliosis is when the curve is from left to right, right to left, or both. Doctors often describe the shape as a ‘C’ or an ‘S’ when looking at your spine from behind. The angle of the curvature can range a lot, but a curvature of the spine over 10 degrees on an x-ray is considered a diagnosis of scoliosis.
This sideways spinal curvature usually starts just before puberty with adolescent growth spurts between 10 and 15 years of age. According to the Mayo Clinic, about 3% of adolescents develop this spinal deformation, or about 1.2 million pre-teens and teens. Scoliosis can be caused by other conditions, but most causes of scoliosis are unknown. Most cases are correctable especially when caught early.
Scoliosis can cause no discomfort to moderate discomfort, but in severe cases, it can cause life-threatening problems such as difficulty breathing. In severe cases, the curve can continue to get worse throughout life, but in most cases, curving stops when the skeleton stops growing after puberty. Scoliosis should be monitored closely to avoid serious progression and greater medical issues.
Common types of scoliosis
Since this disease affects a wide range of people, medical professionals divide scoliosis into four forms of scoliosis. These types are:
- Idiopathic scoliosis is when the cause is unknown. This accounts for up to 80% of scoliosis cases.
- Congenital scoliosis occurs in the mother’s womb before birth. The vertebrae may fail to divide properly or incompletely develop. This type may go unnoticed until after birth or into the teen years.
- Neuromuscular scoliosis is caused by other disorders such as spinal cord injury, cerebral palsy, and others. These conditions can damage your back muscles by not allowing them to support your spine properly sometimes causing your back to curve.
- Degenerative scoliosis, unlike other types of scoliosis, develops in adults. It often occurs in the lower back because as we age, the discs and joints wear out.
- Syndromic scoliosis which is a result of muscular disorders like spina bifida and muscular dystrophy, or connective tissues diseases like Marfan syndrome.
- Thoracogenic scoliosis develops for some people if they received radiation or congenital heart defect surgery in childhood.
Common symptoms of scoliosis
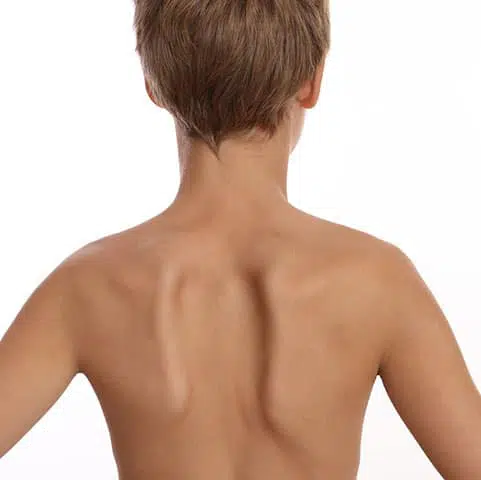
Depending on the severity and location, scoliosis symptoms can vary wildly. The clearest symptom is that your entire body is leaning to one side or the other.
Other common, mild symptoms are often visible and include:
- Difference in hip height
- Difference in rib cage height
- Difference in shoulder height
- One or both shoulder blades stick out
- Head is not centered above the pelvis
- Spinal texture or color changes
- Spinal dimples or hairy patches
More serious cases of scoliosis may cause:
- Back pain or stiffness
- Bowel or bladder dysfunction
- Height loss
- Inability to stand upright
- Leg pain
- Numbness
- Muscle weakness
In more moderate to severe cases, the spine may also twist causing one side of the body’s ribs to stick out further than the other.
Are there risk factors for scoliosis?
There are a few reasons you or your child may develop scoliosis compared to others:
- Age: Other than degenerative scoliosis, by 16 or so, you should know if they will develop it or not.
- Sex: Males and females develop scoliosis at the same rate, but female cases are more likely to worsen.
- Family history: It can sometimes run in families.
Diagnosis and treatment options
Diagnosing scoliosis is quite simple as the curve is noticeable from straight on when looking at the back. A short physical exam of the back will often confirm a diagnosis, but we will often order in-house digital x-rays to have a look at the severity.
At BackFit Health + Spine, we have a variety of treatment options available for you. Depending on the severity and treatment plan to stop the curvature from worsening, treatment may include:
- Anti-Inflammatory medication
- Chiropractic adjustments
- Cortisone shots
- Electrical stimulation
- Epidural steroid injection
- Facet injections
- Inversion therapy
- Physical therapy
- Spinal bracing
- Spinal decompression
- Pain management
- Spinal cord stimulator
- Trigger point injections
Whether you’re concerned about your child with scoliosis or you are an adult living with scoliosis, it is nothing to be ashamed of. While it may interfere with your quality of life, it doesn’t have to. Our trained professionals can help you manage your condition and find relief with a variety of minimally invasive methods without scoliosis surgery. While spinal fusion surgery is necessary in the worst cases, it’s something we aim for you to avoid.
More About BackFit
Looking to learn more? Explore our locations, treatments, or our new patient offer below or contact one of the BackFit Family of staff to have your questions answered.